Classical XY model
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
The classical XY model (sometimes also called classical rotor (rotator) model or O(2) model) is a lattice model of statistical mechanics. In general, the XY model can be seen as a specialization of Stanley's n-vector model[1] for n = 2.
Definition
Given a D-dimensional lattice Λ, per each lattice site j ∈ Λ there is a two-dimensional, unit-length vector sj = (cos θj, sin θj)
The spin configuration, s = (sj)j ∈ Λ is an assignment of the angle −π < θj ≤ π for each j ∈ Λ.
Given a translation-invariant interaction Jij = J(i − j) and a point dependent external field , the configuration energy is
The case in which Jij = 0 except for ij nearest neighbor is called nearest neighbor case.
The configuration probability is given by the Boltzmann distribution with inverse temperature β ≥ 0:
where Z is the normalization, or partition function.[2] The notation indicates the expectation of the random variable A(s) in the infinite volume limit, after periodic boundary conditions have been imposed.
Rigorous results
- The existence of the thermodynamic limit for the free energy and spin correlations were proved by Ginibre, extending to this case the Griffiths inequality.[3]
- Using the Griffiths inequality in the formulation of Ginibre, Aizenman and Simon[4] proved that the two point spin correlation of the ferromagnetics XY model in dimension D, coupling J > 0 and inverse temperature β is dominated by (i.e. has an upper bound given by) the two point correlation of the ferromagnetic Ising model in dimension D, coupling J > 0 and inverse temperature β/2 Hence the critical β of the XY model cannot be smaller than the double of the critical temperature of the Ising model
One dimension
As in any 'nearest-neighbor' n-vector model with free (non-periodic) boundary conditions, if the external field is zero, there exists a simple exact solution. In the free boundary conditions case, the Hamiltonian is

Even in the thermodynamic limit, there is no divergence in the specific heat. Indeed, like the one-dimensional Ising model, the one-dimensional XY model has no phase transitions at finite temperature.
The same computation for periodic boundary condition (and still h = 0) requires the transfer matrix formalism, though the result is the same.[6]
The partition function can be evaluated as
This transfer matrix approach is also required when using free boundary conditions, but with an applied field . If the applied field is small enough that it can be treated as a perturbation to the system in zero-field, then the magnetic susceptibility can be estimated. This is done by using the eigenstates computed by the transfer matrix approach and computing the energy shift with second-order perturbation theory, then comparing with the free-energy expansion . One finds [7]
Two dimensions
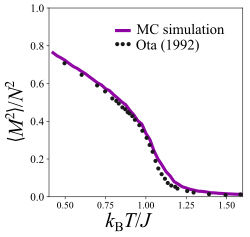
The two-dimensional XY model with nearest-neighbor interactions is an example of a two-dimensional system with continuous symmetry that does not have long-range order. Likewise, there is not a conventional phase transition present that would be associated with symmetry breaking. However, as will be discussed later, the system does show signs of a transition from a disordered high-temperature state to a quasi-ordered state below some critical temperature, called the Kosterlitz-Thouless transition. In the case of a discrete lattice of spins, the two-dimensional XY model can be evaluated using the transfer matrix approach, reducing the model to an eigenvalue problem and utilizing the largest eigenvalue from the transfer matrix. Though the exact solution is intractable, it is possible to use certain approximations to get estimates for the critical temperature which occurs at low temperatures. For example, Mattis (1984[9]) used an approximation to this model to estimate a critical temperature of the system as

Furthermore, using statistical mechanics one can relate thermodynamic averages to quantities like specific heat by calculating
The nature of the critical transitions and vortex formation can be elucidated by considering a continuous version of the XY model. Here, the discrete spins are replaced by a field representing the spin's angle at any point in space. In this case the angle of the spins must vary smoothly over changes in position. Expanding the original cosine as a Taylor series, the Hamiltonian can be expressed in the continuum approximation as

The continuous version of the XY model is often used to model systems that possess order parameters with the same kinds of symmetry, e.g. superfluid helium, hexatic liquid crystals. This is what makes them peculiar from other phase transitions which are always accompanied with a symmetry breaking. Topological defects in the XY model lead to a vortex-unbinding transition from the low-temperature phase to the high-temperature disordered phase. Indeed, the fact that at high temperature correlations decay exponentially fast, while at low temperatures decay with power law, even though in both regimes M(β) = 0, is called Kosterlitz–Thouless transition. Kosterlitz and Thouless provided a simple argument of why this would be the case: this considers the ground state consisting of all spins in the same orientation, with the addition then of a single vortex. The presence of these contributes an entropy of roughly , where is an effective length scale (for example, the lattice size for a discrete lattice) Meanwhile, the energy of the system increases due to the vortex, by an amount . Putting these together, the free energy of a system would change due to the spontaneous formation of a vortex by an amount
To visualize the Ising model, one can use an arrow pointing up or down, or represented as a point colored black/white to indicate its state. To visualize the XY spin system, the spins can be represented as an arrow pointing in some direction, or as being represented as a point with some color. Here it is necessary to represent the spin with a spectrum of colors due to each of the possible continuous variables. This can be done using, for example, a continuous and periodic red-green-blue spectrum. As shown on the figure, cyan corresponds to a zero angle (pointing to the right), whereas red corresponds to a 180 degree angle (pointing to the left). One can then study snapshots of the spin configurations at different temperatures to elucidate what happens above and below the critical temperature of the XY model. At high temperatures, the spins will not have a preferred orientation and there will be unpredictable variation of angles between neighboring spins, as there will be no preferred energetically favorable configuration. In this case, the color map will look highly pixellated. Meanwhile at low temperatures, one possible ground-state configuration has all spins pointed in the same orientation (same angle); these would correspond to regions (domains) of the color map where all spins have roughly the same color.

To identify vortices (or antivortices) present as a result of the Kosterlitz–Thouless transition, one can determine the signed change in angle by traversing a circle of lattice points counterclockwise. If the total change in angle is zero, this corresponds to no vortex being present; whereas a total change in angle of corresponds to a vortex (or antivortex). These vortexes are topologically non-trivial objects that come in vortex-antivortex pairs, which can separate or pair-annihilate. In the colormap, these defects can be identified in regions where there is a large color gradient where all colors of the spectrum meet around a point. Qualitatively, these defects can look like inward- or outward-pointing sources of flow, or whirlpools of spins that collectively clockwise or counterclockwise, or hyperbolic-looking features with some spins pointing toward and some spins pointing away from the defect. As the configuration is studied at long time scales and at low temperatures, it is observed that many of these vortex-antivortex pairs get closer together and eventually pair-annihilate. It is only at high temperatures that these vortices and antivortices are liberated and unbind from one another.
In the continuous XY model, the high-temperature spontaneous magnetization vanishes:
while McBryan and Spencer found the upper bound, for any
Three and higher dimensions
Independently of the range of the interaction, at low enough temperature the magnetization is positive.
- At high temperature, the spontaneous magnetization vanishes: . Besides, cluster expansion shows that the spin correlations cluster exponentially fast: for instance .
- At low temperature, infrared bound shows that the spontaneous magnetization is strictly positive: . Besides, there exists a 1-parameter family of extremal states, , such that but, conjecturally, in each of these extremal states the truncated correlations decay algebraically.
Phase transition
As mentioned above in one dimension the XY model does not have a phase transition, while in two dimensions it has the Berezinski-Kosterlitz-Thouless transition between the phases with exponentially and powerlaw decaying correlation functions.
In three and higher dimensions the XY model has a ferromagnet-paramagnet phase transition. At low temperatures the spontaneous magnetization is nonzero: this is the ferromagnetic phase. As the temperature is increased, spontaneous magnetization gradually decreases and vanishes at a critical temperature. It remains zero at all higher temperatures: this is the paramagnetic phase.
In four and higher dimensions the phase transition has mean field theory critical exponents (with logarithmic corrections in four dimensions).
Three dimensional case: the critical exponents
The three dimensional case is interesting because the critical exponents at the phase transition are nontrivial. Many three-dimensional physical systems belong to the same universality class as the three dimensional XY model and share the same critical exponents, most notably easy-plane magnets and liquid Helium-4. The values of these critical exponents are measured by experiments, Monte Carlo simulations, and can also be computed by theoretical methods of quantum field theory, such as the renormalization group and the conformal bootstrap. Renormalization group methods are applicable because the critical point of the XY model is believed to be described by a renormalization group fixed point. Conformal bootstrap methods are applicable because it is also believed to be a unitary three dimensional conformal field theory.
Most important critical exponents of the three dimensional XY model are . All of them can be expressed via just two numbers: the scaling dimensions and of the complex order parameter field and of the leading singlet operator (same as in the Ginzburg–Landau description). Another important field is (same as ), whose dimension determines the correction-to-scaling exponent . According to a conformal bootstrap computation,[15] these three dimensions are given by:
| 0.519088(22) | |
| 1.51136(22) | |
| 3.794(8) |
This gives the following values of the critical exponents:
| general expression () | numerical value | |
|---|---|---|
| α | -0.01526(30) | |
| β | 0.34869(7) | |
| γ | 1.3179(2) | |
| δ | 4.77937(25) | |
| η | 0.038176(44) | |
| ν | 0.67175(10) | |
| ω | 0.794(8) |
Monte Carlo methods give compatible determinations:[16] .
See also
- Classical Heisenberg model
- Coulomb gas
- Goldstone boson
- Ising model
- Potts model
- n-vector model
- Kosterlitz–Thouless transition
- Topological defect
- Superfluid film
- Sigma model
- Sine-Gordon model
Notes
- ^ Stanley, H.E. (1968). "Dependence of Critical Properties on Dimensionality of Spins". Physical Review Letters. 20 (12): 589–592. Bibcode:1968PhRvL..20..589S. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.20.589.
- ^ Chaikin, P.M.; Lubensky, T.C. (2000). Principles of Condensed Matter Physics. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0521794503.
- ^ Ginibre, J. (1970). "General formulation of Griffiths' inequalities". Communications in Mathematical Physics. 16 (4): 310–328. Bibcode:1970CMaPh..16..310G. doi:10.1007/BF01646537. S2CID 120649586.
- ^ Aizenman, M.; Simon, B. (1980). "A comparison of plane rotor and Ising models". Physics Letters A. 76 (3–4): 281–282. Bibcode:1980PhLA...76..281A. doi:10.1016/0375-9601(80)90493-4.
- ^ Badalian, D. (1996). "On the thermodynamics of classical spins with isotrop Heisenberg interaction in one-dimensional quasi-periodic structures". Physica B. 226 (4): 385–390. Bibcode:1996PhyB..226..385B. doi:10.1016/0921-4526(96)00283-9.
- ^ Mattis, D.C. (1984). "Transfer matrix in plane-rotator model". Physics Letters A. 104 A (6–7): 357–360. Bibcode:1984PhLA..104..357M. doi:10.1016/0375-9601(84)90816-8.
- ^ Mattis, D. C. (1985). The Theory of Magnetism II. Springer Series in Solid-State Physics. ISBN 978-3-642-82405-0.
- ^ Ota, S.; Ota, S.B.; Fahnle, M (1992). "Microcanonical Monte Carlo simulations for the two-dimensional XY model". Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter. 4 (24): 5411. Bibcode:1992JPCM....4.5411O. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/4/24/011. S2CID 250920391.
- ^ Mattis, Daniel (1984). "Transfer matrix in plane-rotator model". Physics Letters A. 104 (6–7): 357–360.
- ^ Hsieh, Y.-D.; Kao, Y.-J.; Sandvik, A.W. (2013). "Finite-size scaling method for the Berezinskii-Kosterlitz-Thouless transition". Journal of Statistical Mechanics: Theory and Experiment. 2013 (9): P09001. arXiv:1302.2900. Bibcode:2013JSMTE..09..001H. doi:10.1088/1742-5468/2013/09/P09001. S2CID 118609225.
- ^ Nguyen, P.H.; Boninsegni, M. (2021). "Superfluid Transition and Specific Heat of the 2D x-y Model: Monte Carlo Simulation". Applied Sciences. 11 (11): 4931. arXiv:2105.14112. doi:10.3390/app11114931.
- ^ Tobochnik, J.; Chester, G.V. (1979). "Monte Carlo study of the planar spin model". Physical Review B. 20 (9): 3761–3769. Bibcode:1979PhRvB..20.3761T. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.20.3761.
- ^ Binder, K. (2013). Applications of the Monte Carlo Method in Statistical Physics. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 978-3-642-51703-7.
- ^ Fröhlich, J.; Spencer, T. (1981). "The Kosterlitz–Thouless transition in two-dimensional abelian spin systems and the Coulomb gas". Communications in Mathematical Physics. 81 (4): 527–602. Bibcode:1981CMaPh..81..527F. doi:10.1007/bf01208273. S2CID 73555642.
- ^ Chester, Shai M.; Landry, Walter; Liu, Junyu; Poland, David; Simmons-Duffin, David; Su, Ning; Vichi, Alessandro (2020). "Carving out OPE space and precise O(2) model critical exponents". Journal of High Energy Physics. 2020 (6): 142. arXiv:1912.03324. Bibcode:2020JHEP...06..142C. doi:10.1007/JHEP06(2020)142. ISSN 1029-8479. S2CID 208910721.
- ^ Hasenbusch, Martin (2019-12-26). "Monte Carlo study of an improved clock model in three dimensions". Physical Review B. 100 (22): 224517. arXiv:1910.05916. Bibcode:2019PhRvB.100v4517H. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.100.224517. ISSN 2469-9950. S2CID 204509042.
References
- Evgeny Demidov, Vortices in the XY model (2004)
Further reading
- H. E. Stanley, Introduction to Phase Transitions and Critical Phenomena, (Oxford University Press, Oxford and New York 1971);
- H. Kleinert, Gauge Fields in Condensed Matter, Vol. I, " SUPERFLOW AND VORTEX LINES", pp. 1–742, Vol. II, "STRESSES AND DEFECTS", pp. 743–1456, World Scientific (Singapore, 1989); Paperback ISBN 9971-5-0210-0 (also available online: Vol. I and Vol. II)


![{\displaystyle P(\mathbf {s} )={\frac {e^{-\beta H(\mathbf {s} )}}{Z}}\qquad Z=\int _{[-\pi ,\pi ]^{\Lambda }}\prod _{j\in \Lambda }d\theta _{j}\;e^{-\beta H(\mathbf {s} )}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/71ef5f2950de7a5f4eb1d1eacee3cd891b7ea028)



![{\displaystyle H(\mathbf {s} )=-J[\cos(\theta _{1}-\theta _{2})+\cdots +\cos(\theta _{L-1}-\theta _{L})]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1c073664bcdcef4270af90ece05425114d25b43c)

![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}Z&=\int _{-\pi }^{\pi }d\theta _{1}\cdots d\theta _{L}\;e^{\beta J\cos(\theta _{1}-\theta _{2})}\cdots e^{\beta J\cos(\theta _{L-1}-\theta _{L})}\\&=2\pi \prod _{j=2}^{L}\int _{-\pi }^{\pi }d\theta '_{j}\;e^{\beta J\cos \theta '_{j}}=(2\pi )\left[\int _{-\pi }^{\pi }d\theta '_{j}\;e^{\beta J\cos \theta '_{j}}\right]^{L-1}=(2\pi )^{L}(I_{0}(\beta J))^{L-1}\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/75a41062f2bd4551ebe2affdddaed54033d95f2f)


![{\displaystyle f(\beta ,h=0)=-\lim _{L\to \infty }{\frac {1}{\beta L}}\ln Z=-{\frac {1}{\beta }}\ln[2\pi I_{0}(\beta J)]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/fef0b98102ed3e9d32986fb1205efd82c47936c3)












![{\displaystyle Z=[2\pi I_{0}(\beta J)]^{L}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/888ecca89dd7e964668cafd70f8c1da8756baf56)



























![{\displaystyle (-\pi ,\pi ]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7fbb1843079a9df3d3bbcce3249bb2599790de9c)
































