Howrah–Chennai Mail
| Overview | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Service type | |||||
| Locale | West Bengal, Orissa, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu | ||||
| First service | 15 August 1900 | ||||
| Current operator(s) | South Eastern Railway zone | ||||
| Route | |||||
| Termini | Howrah Junction Chennai Central | ||||
| Distance travelled | 1,664 km (1,034 mi) | ||||
| Average journey time | 27 hours Approx. | ||||
| Service frequency | Daily | ||||
| Train number(s) | 12839 / 12840 | ||||
| On-board services | |||||
| Class(es) | AC First, AC 2 Tier, AC 3 Tier, Sleeper Class, General Unreserved | ||||
| Seating arrangements | Yes | ||||
| Sleeping arrangements | Yes | ||||
| Catering facilities | Yes | ||||
| Observation facilities | Large windows | ||||
| Baggage facilities | Yes | ||||
| Technical | |||||
| Rolling stock | LHB coach | ||||
| Track gauge | 1,676 mm (5 ft 6 in) | ||||
| Operating speed | 59 km/h (37 mph) average with halts | ||||
| |||||
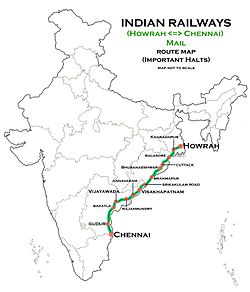
The 12839 / 12840 Howrah-Chennai Mail is a mail train of Indian Railways connecting Howrah Junction and Chennai Central. It connects three metropolitan cities of India, Kolkata, Chennai and Visakhapatnam. It also runs via some major cities of India like Bhubaneswar, Vijayawada, etc.
The second-most preferred train to the south after Coromandel Express'.'
History
The train made its inaugural run on August 15, 1900, which makes it one of the oldest running trains on Indian railways. It was first hauled by steam engines, including the WP class engines, then by diesel, and now by electric WAP-4 or WAP-7 locomotives. It was the first passenger train to be dieselized on the South Eastern Railway in 1964–65. Till the introduction of the Coromandel Express in the mid-seventies, it was the main and fastest train link between Howrah and Chennai (then Madras), with much fewer halts. Presently, this train is the second most important train on the Howrah–Chennai main line after the high speed Coromandel Express. It covers 1,664 km (1,034 mi) at an average speed of 59 km/h (37 mph)
Rakes
- 3 AC Two Tier
- 8 AC Three Tier
- 3 AC Three Tier Economy
- 3 Sleeper class
- 1 Pantry car
- 2 General Unreserved
- 1 End on Generation car (EOG)
- 1 Sitting luggage cum brake van (SLR)
| Loco | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 22 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLR | H1 | A1 | A2 | M1 | M2 | B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | B6 | B7 | B8 | PC | S1 | S2 | S3 | GS | GS | EOG |
Route
Important stations through which it passes are Kharagpur Junction, Balasore, Cuttack Junction, Bhubaneswar, Khurda Road Junction, Berhampur, Naupada, Srikakulam Road railway station , Visakhapatnam, Samalkot Junction, Rajahmundry, Eluru, Vijayawada Junction, Tenali Junction, Nellore, Gudur Junction.
References
- Short description with empty Wikidata description
- Use Indian English from December 2013
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- All Wikipedia articles written in Indian English
- Use dmy dates from December 2023
- Express trains in India
- Mail trains in India
- Rail transport in Andhra Pradesh
- Rail transport in Odisha
- Rail transport in Tamil Nadu
- Rail transport in West Bengal
- Railway services introduced in 1900
- Transport in Chennai
- Rail transport in Howrah
- Indian express train stubs