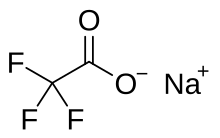
Sodium trifluoroacetate
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Sodium trifluoroacetate
| |
| Other names
Sodium perfluoroacetate
Sodium 2,2,2-trifluoroacetate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2F3NaO2 | |
| Molar mass | 136.005 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
| Density | 1.49 g mL−1 |
| Melting point | 207 °C (405 °F; 480 K) |
| Boiling point | Decomposes |
| 625 g/L | |
| Solubility | soluble in alcohol, acetonitrile, dimethylformamide and most of polar organic solvents |
| Acidity (pKa) | 0.23 (conjugate acid) |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Toxic, Irritant, Harmful to environment |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H300, H315, H319, H335, H410 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P301+P310, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | <imagemap>
File:NFPA 704.svg|80px|alt=NFPA 704 four-colored diamond poly 150 150 300 300 150 450 0 300 Health 2: Intense or continued but not chronic exposure could cause temporary incapacitation or possible residual injury. E.g. chloroform poly 300 0 450 150 300 300 150 150 Flammability 0: Will not burn. E.g. water poly 450 150 600 300 450 450 300 300 Instability 1: Normally stable, but can become unstable at elevated temperatures and pressures. E.g. calcium poly 300 300 450 450 300 600 150 450 Special hazards (white): no code desc none </imagemap> |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Non-flammable | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Sodium trichloroacetate |
Other cations
|
Lithium trifluoroacetate Potassium trifluoroacetate |
Related compounds
|
Sodium formate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Sodium trifluoroacetate is a chemical compound with a formula of CF3CO2Na. It is the sodium salt of trifluoroacetic acid. It is used as a source of trifluoromethylations.[1]
Basicity
With a pKa of 0.23 for trifluoroacetic acid, the trifluoroacetate ion is an extremely weak base compared to acetic acid, which has a pKa of 4.76. This is due to the electron-withdrawing effect of the three fluorine atoms adjacent the carboxylate group. Strong acids such as hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid can protonate the trifluoroacetate ion to trifluoroacetic acid:
In general, trifluoroacetate reacts in equilibrium with hydronium cations to form trifluoroacetic acid:
The general reaction with hydronium is in equilibrium due to the similarity in pKa between trifluoroacetic acid and the hydronium ion.
Preparation
One convenient method is by dissolving an equivalent amount of sodium carbonate in 50% aqueous solution of trifluoroacetic acid. The solution is filtered and evaporated by vacuum evaporation (with special care to avoid decomposition of the salt by overheating). The solid obtained is dried under vacuum at 100 °C.[2]
Uses
Sodium trifluoroacetate is a useful reagent for trifluoromethylation.
See also
References
- ^ Chang, Ying; Cai, Chun (June 2005). "Trifluoromethylation of carbonyl compounds with sodium trifluoroacetate". Journal of Fluorine Chemistry. 126 (6): 937–940. doi:10.1016/j.jfluchem.2005.04.012.
- ^ Prakash, G. K. Surya; Mathew, Thomas (2010), "Sodium Trifluoroacetate", Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis, doi:10.1002/047084289x.rn01136, ISBN 9780470842898



