split (Unix)
This article is written like a manual or guide. (June 2013) |
 Example of split usage | |
| Original author(s) | AT&T Bell Laboratories |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Various open-source and commercial developers |
| Initial release | February 1973 |
| Written in | C |
| Operating system | Unix, Unix-like, Plan 9, IBM i |
| Platform | Cross-platform |
| Type | Command |
| License | coreutils: GPLv3+ Plan 9: MIT License |
split is a utility on Unix, Plan 9, and Unix-like operating systems most commonly used to split a computer file into two or more smaller files.
History
The <syntaxhighlight lang="text" class="" style="" inline="1">split</syntaxhighlight> command first appeared in Version 3 Unix[1] and is part of the X/Open Portability Guide since issue 2 of 1987. It was inherited into the first version of POSIX.1 and the Single Unix Specification.[2] The version of split bundled in GNU coreutils was written by Torbjorn Granlund and Richard Stallman.[3] The split command has also been ported to the IBM i operating system.[4]
Usage
The command-syntax is: <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
split [OPTION] [INPUT [PREFIX]]
</syntaxhighlight>
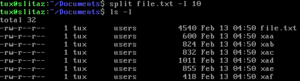
The default behavior of split is to generate output files of a fixed size, default 1000 lines. The files are named by appending aa, ab, ac, etc. to output filename. If output filename is not given, the default filename of x is used, for example, xaa, xab, etc. When a hyphen (-) is used instead of input filename, data is derived from standard input. The files are typically rejoined using a utility such as cat.
Additional program options permit a maximum character count (instead of a line count), a maximum line length, how many incrementing characters in generated filenames, and whether to use letters or digits.
Split file into pieces
Create a file named "myfile.txt" with exactly 3,000 lines of data:
<syntaxhighlight lang="console">
$ head -3000 < /dev/urandom > myfile.txt
</syntaxhighlight>
Now, use the split command to break this file into pieces (note: unless otherwise specified, split will break the file into 1,000-line files):
<syntaxhighlight lang="console">
$ split myfile.txt
$ ls -l
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 761K Jun 16 18:17 myfile.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 242K Jun 16 18:17 xaa
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 263K Jun 16 18:17 xab
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 256K Jun 16 18:17 xac
$ wc --lines xa*
1000 xaa 1000 xab 1000 xac 3000 total
</syntaxhighlight>
As seen above, the split command has broken the original file (keeping the original intact) into three, equal in number of lines (i.e., 1,000), files: xaa, xab, and xac.
See also
- csplit – splits by content rather than by size
- File spanning
- List of Unix commands
References
- ^ – FreeBSD General Commands Manual
- ^ – Shell and Utilities Reference, The Single UNIX Specification, Version 4 from The Open Group
- ^ "split(1): split file into pieces - Linux man page". linux.die.net.
- ^ IBM. "IBM System i Version 7.2 Programming Qshell" (PDF). IBM. Retrieved 2020-09-05.
External links
- – Shell and Utilities Reference, The Single UNIX Specification, Version 4 from The Open Group