Prothipendyl
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
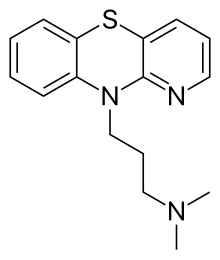
| Preferred IUPAC name
N,N-Dimethyl-3-(10H-pyrido[3,2-b][1,4]benzothiazin-10-yl)propan-1-amine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H19N3S | |
| Molar mass | 285.40716 |
| Pharmacology | |
| N05AX07 (WHO) | |
| Legal status | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Prothipendyl (brand names Dominal, Timovan, Tolnate), also known as azapromazine or phrenotropin, is an anxiolytic, antiemetic, and antihistamine of the azaphenothiazine group which is marketed in Europe and is used to treat anxiety and agitation in psychotic syndromes.[2][3][4][5] It differs from promazine only by the replacement of one carbon atom with a nitrogen atom in the tricyclic ring system.[2][3] Prothipendyl is said to not possess antipsychotic effects, and in accordance, appears to be a weaker dopamine receptor antagonist than other phenothiazines.[6][5]
Synthesis
See also: Pipazetate.

1-Azaphenothiazine [261-96-1] (1) 3-Dimethylaminopropyl chloride [109-54-6] (2) Sodium hydride suspension
References
- ^ Anvisa (2023-03-31). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in português do Brasil). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-04-04). Archived from the original on 2023-08-03. Retrieved 2023-08-16.
- ^ 2.0 2.1 J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 1038–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- ^ 3.0 3.1 Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. 2000. pp. 893–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2017-09-27. Retrieved 2017-09-27.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ 5.0 5.1 D. Leigh; C.M. Pare; J. Marks (6 December 2012). A Concise Encyclopaedia of Psychiatry. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 396–. ISBN 978-94-011-5913-5.
- ^ Psychotropic Agents: Part I: Antipsychotics and Antidepressants. Springer Science & Business Media. 6 December 2012. pp. 131–. ISBN 978-3-642-67538-6.
- ^ von Schlichtegroll, Proc. 1st Int. Congr. Neuro-Pharm. 1958, 408 (1959), C.A. 54, 13400g (1960).
- ^ Yale, Harry L.; Sowinski, Francis (1958). "10-(Dialkylaminoalkyl)-pyrido[3,2-b][1,4]benzothiazine (1-Azaphenothiazine) and Related Compounds". Journal of the American Chemical Society 80 (7): 1651–1654. doi:10.1021/ja01540a035.
- ^ Yale, Bernstein, U.S. patent 2,943,086 (1960 to Olin Mathieson).
- ^ FR 1173134 (1959 to Rhône-Poulenc).
Categories:
- CS1 português do Brasil-language sources (pt-br)
- CS1 maint: archived copy as title
- Articles without EBI source
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles with changed InChI identifier
- Short description with empty Wikidata description
- Antiemetics
- Anxiolytics
- H1 receptor antagonists
- Hypnotics
- Phenothiazines
- Sedatives
- Psychoactive drug stubs