From English Wikipedia @ Freddythechick
Chemical element with atomic number 31 (Ga)
Gallium, 31 Ga Pronunciation (GAL -ee-əm Appearance silvery blue
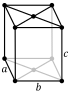
Atomic number (Z ) 31 Group group 13 (boron group) Period period 4 Block p-block Electron configuration [Ar ] 3d10 4s2 4p1 Electrons per shell 2, 8, 18, 3 Phase at STP solid Melting point 302.9146 K (29.7646 °C, 85.5763 °F) Boiling point 2676 K (2403 °C, 4357 °F)[3] [4] Density (at 20° C) 5.907 g/cm3 [5] when liquid (at m.p. ) 6.095 g/cm3 Heat of fusion 5.59 kJ/mol Heat of vaporization 256 kJ/mol[3] Molar heat capacity 25.86 J/(mol·K) Vapor pressure
P (Pa)
1
10
100
1 k
10 k
100 k
at T (K)
1310
1448
1620
1838
2125
2518
Oxidation states −5, −4, −3,[6] +3 [7] amphoteric oxide) Electronegativity Pauling scale: 1.81 Ionization energies 1st: 578.8 kJ/mol 2nd: 1979.3 kJ/mol 3rd: 2963 kJ/mol (more ) Atomic radius empirical: 135 pm Covalent radius 122±3 pm Van der Waals radius 187 pm Spectral lines of galliumNatural occurrence primordial Crystal structure base-centered orthorhombic (oS8 ) Lattice constants a = 452.05 pmb = 766.25 pmc = 452.66 pm (at 20 °C)[5] Thermal expansion × 10−6 [5] [a] Thermal conductivity 40.6 W/(m⋅K) Electrical resistivity 270 nΩ⋅m (at 20 °C) Magnetic ordering diamagnetic Molar magnetic susceptibility × 10−6 3 /mol (at 290 K)[8] Young's modulus 9.8 GPa Speed of sound thin rod 2740 m/s (at 20 °C) Poisson ratio 0.47 Mohs hardness 1.5 Brinell hardness 56.8–68.7 MPa CAS Number 7440-55-3 Naming after Gallia Prediction Dmitri Mendeleev (1871) Discovery and first isolationLecoq de Boisbaudran (1875)
Category: Gallium references
child table, as reused in {IB-Ga}
Notes
^ The thermal expansion is anisotropic : the parameters (in the range 280–302.9 K) are αa × 10−6 b × 10−6 c × 10−6 average = × 10−6 [5]
References These references will appear in the article, but this list appears only on this page.
^ "Standard Atomic Weights: Gallium" . CIAAW . 1987.^ Prohaska, Thomas; Irrgeher, Johanna; Benefield, Jacqueline; Böhlke, John K.; Chesson, Lesley A.; Coplen, Tyler B.; Ding, Tiping; Dunn, Philip J. H.; Gröning, Manfred; Holden, Norman E.; Meijer, Harro A. J. (2022-05-04). "Standard atomic weights of the elements 2021 (IUPAC Technical Report)" . Pure and Applied Chemistry . doi :10.1515/pac-2019-0603 . ISSN 1365-3075 . ^ 3.0 3.1 Zhang Y; Evans JRG; Zhang S (2011). "Corrected Values for Boiling Points and Enthalpies of Vaporization of Elements in Handbooks" . J. Chem. Eng. Data . 56 (2): 328–337. doi :10.1021/je1011086 . ^ "Gallium (CAS Number 7440-55-3) : Strem Product Catalog" . Strem Chemicals Inc . Retrieved 4 December 2023 .^ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Arblaster, John W. (2018). Selected Values of the Crystallographic Properties of Elements . Materials Park, Ohio: ASM International. ISBN 978-1-62708-155-9 ^ Ga(−3) has been observed in LaGa, see Dürr, Ines; Bauer, Britta; Röhr, Caroline (2011). "Lanthan-Triel/Tetrel-ide La(Al,Ga)x 1-x . Experimentelle und theoretische Studien zur Stabilität intermetallischer 1:1-Phasen" (PDF) . Z. Naturforsch. (in Deutsch). 66b : 1107–1121.
^ Hofmann, Patrick (1997). Colture. Ein Programm zur interaktiven Visualisierung von Festkörperstrukturen sowie Synthese, Struktur und Eigenschaften von binären und ternären Alkali- und Erdalkalimetallgalliden (PDF) (Thesis) (in Deutsch). PhD Thesis, ETH Zurich. p. 72. doi :10.3929/ethz-a-001859893 . hdl :20.500.11850/143357 . ISBN 978-3728125972 ^ Weast, Robert (1984). CRC, Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . Boca Raton, Florida: Chemical Rubber Company Publishing. pp. E110. ISBN 0-8493-0464-4 ^ 9.0 9.1 Kondev, F. G.; Wang, M.; Huang, W. J.; Naimi, S.; Audi, G. (2021). "The NUBASE2020 evaluation of nuclear properties" (PDF) . Chinese Physics C . 45 (3): 030001. doi :10.1088/1674-1137/abddae . Lua error in mw.title.lua at line 229: too many expensive function calls.